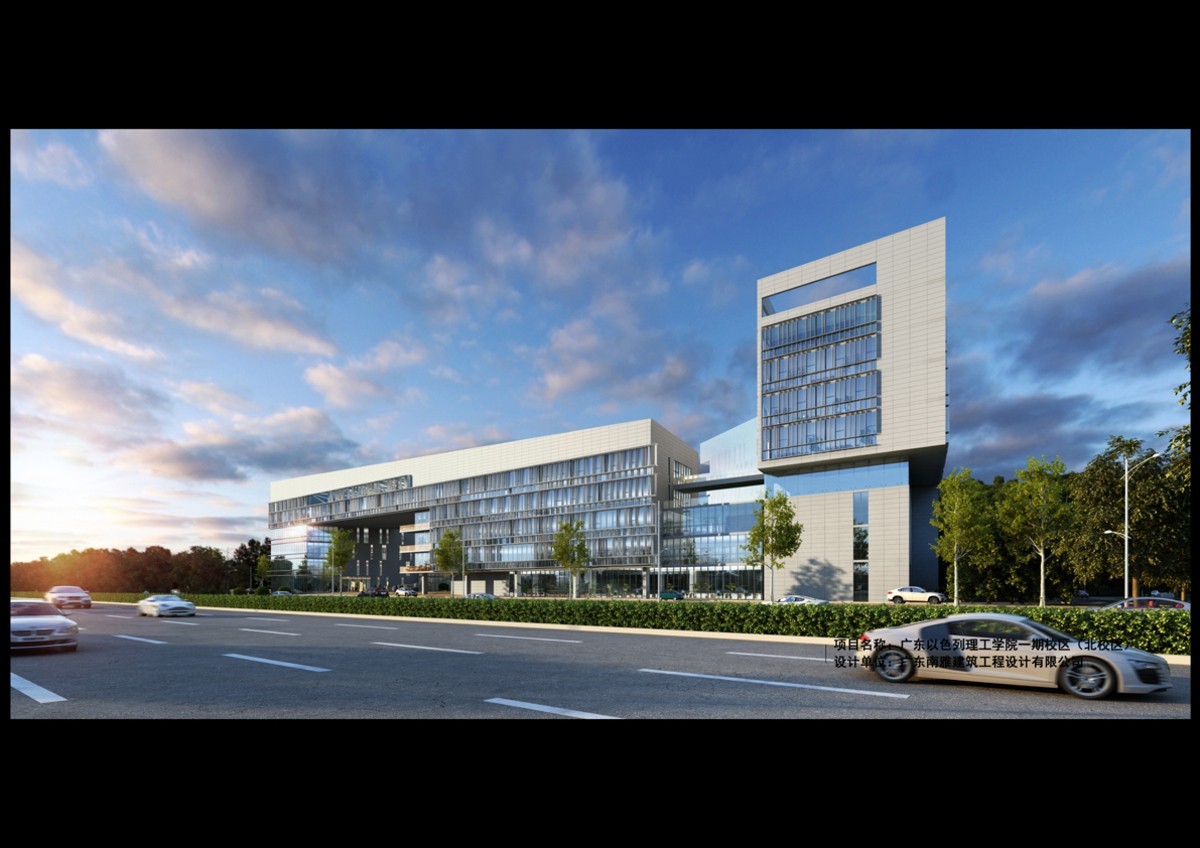
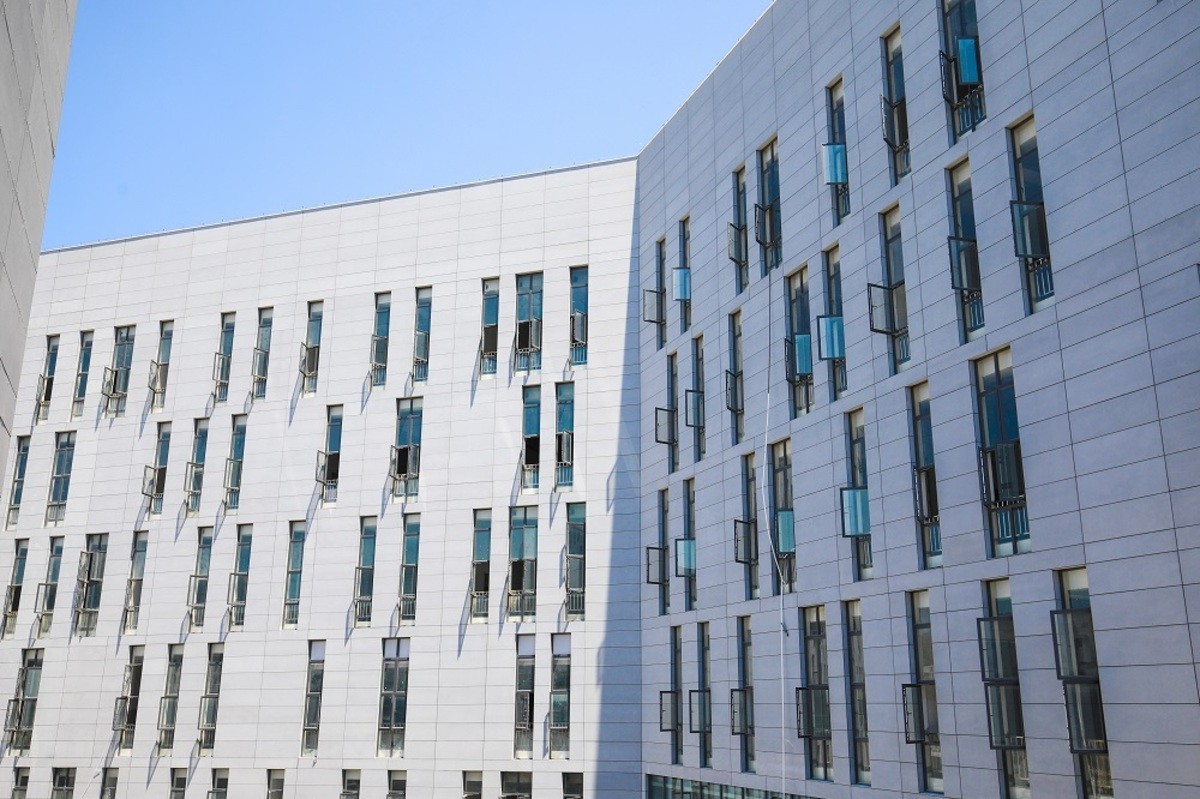
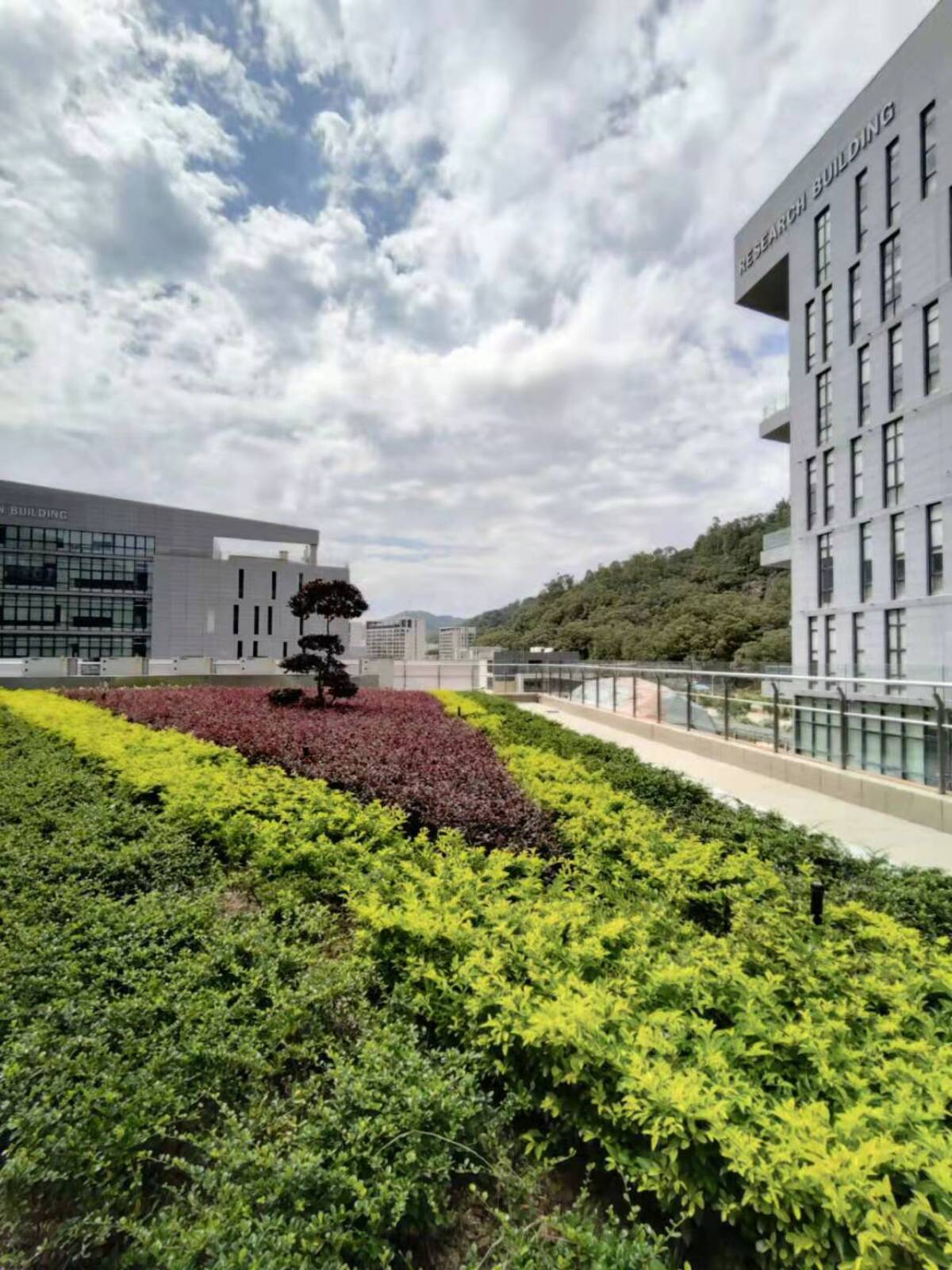
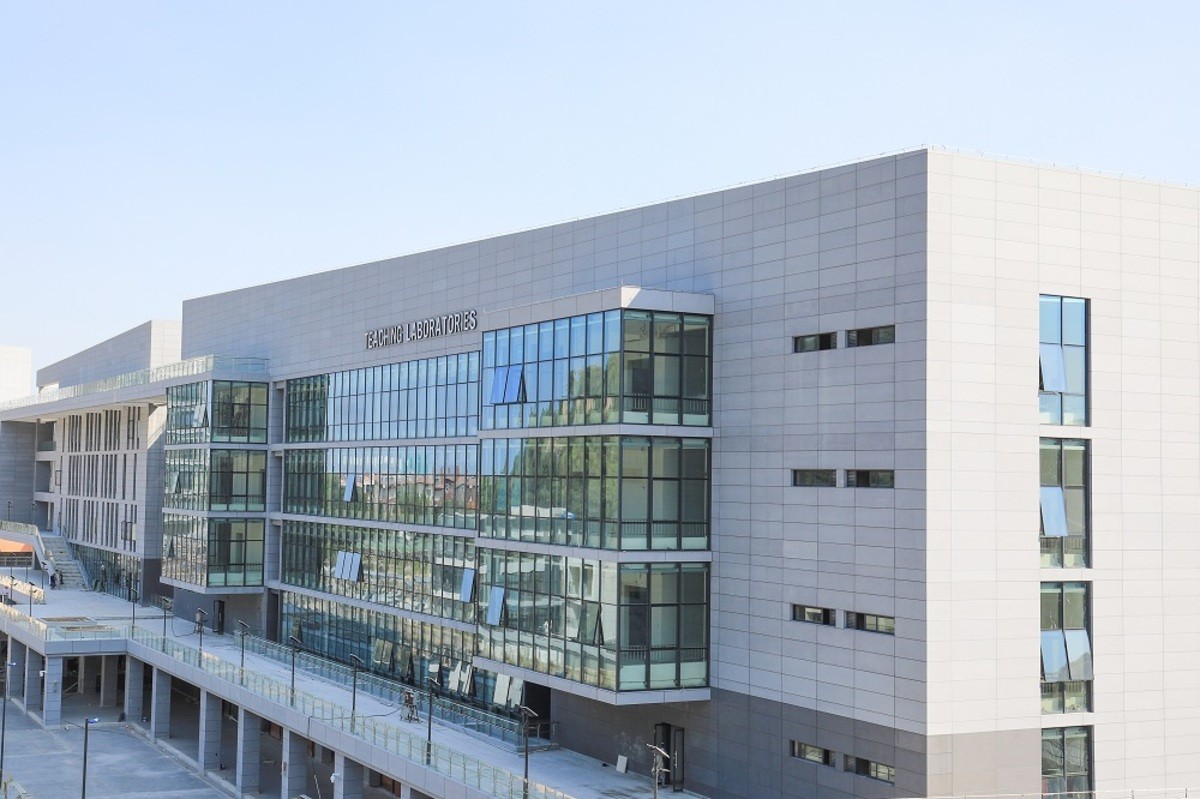
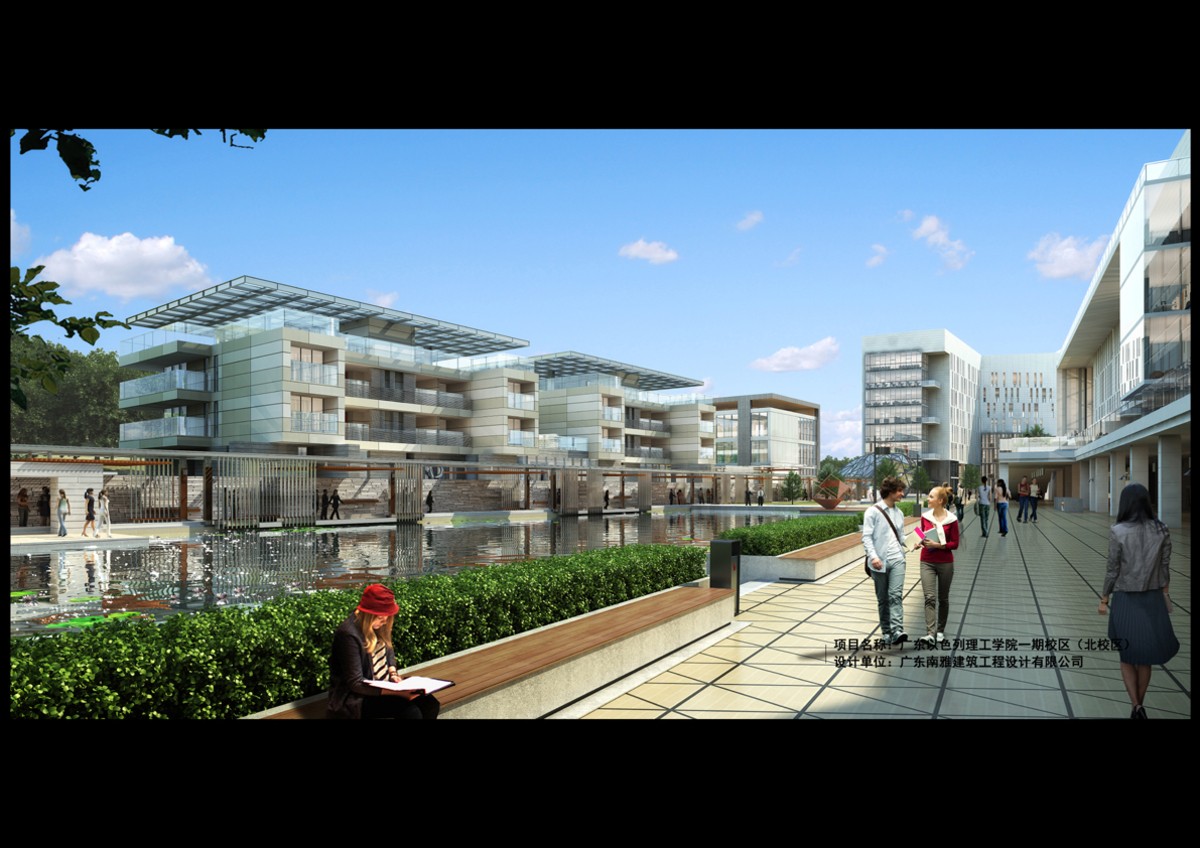
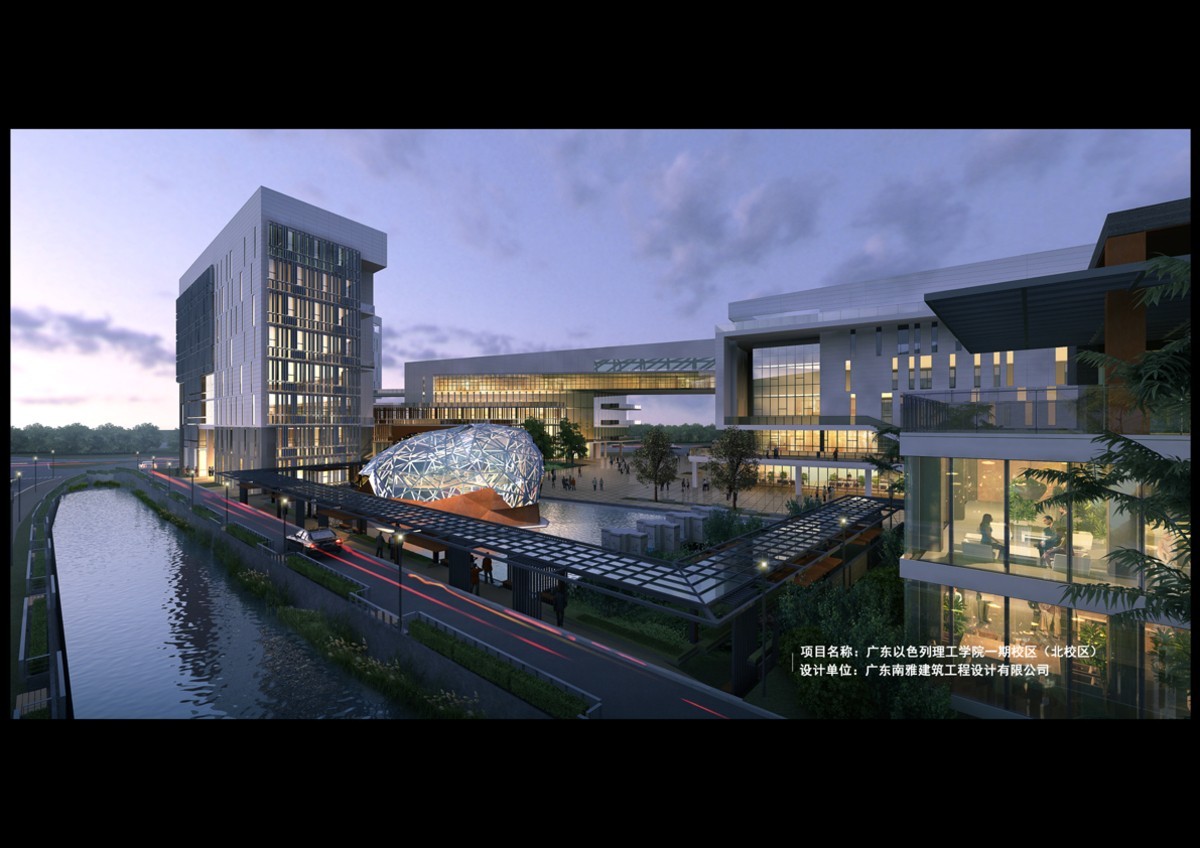
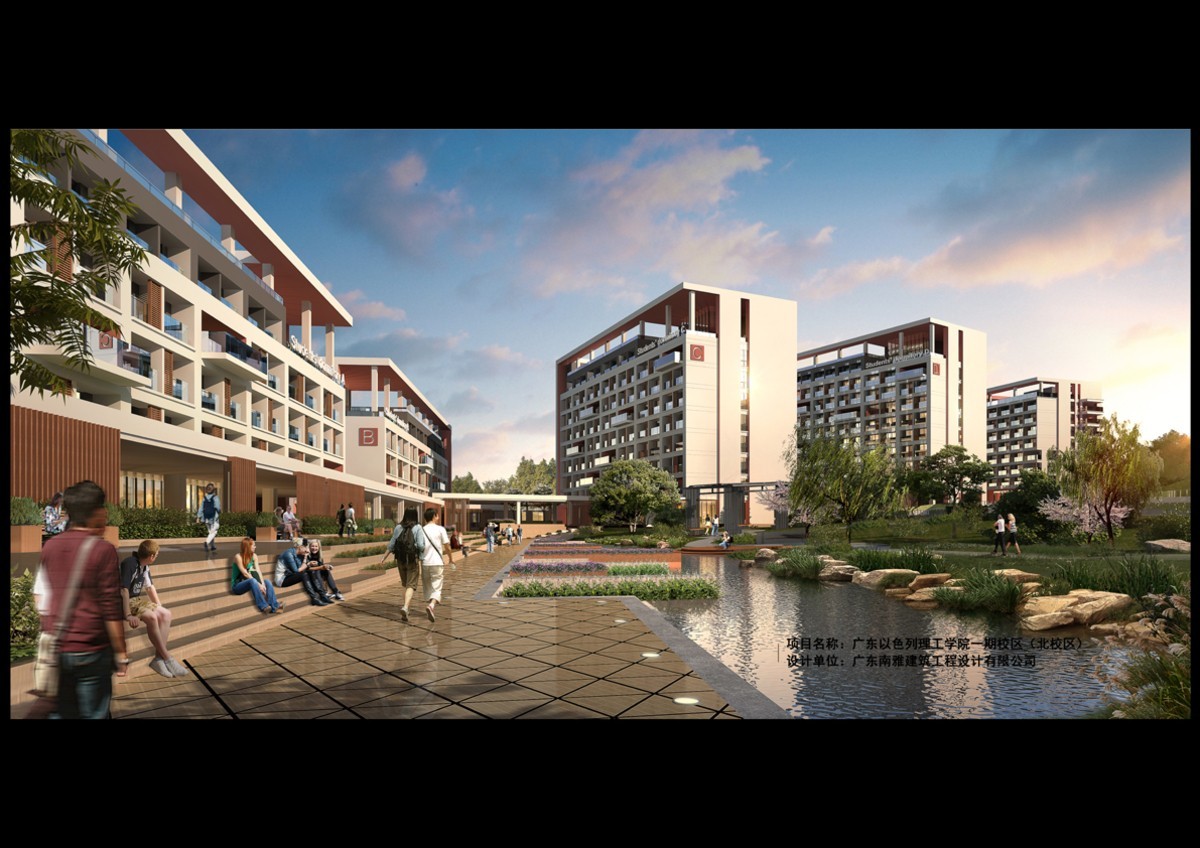
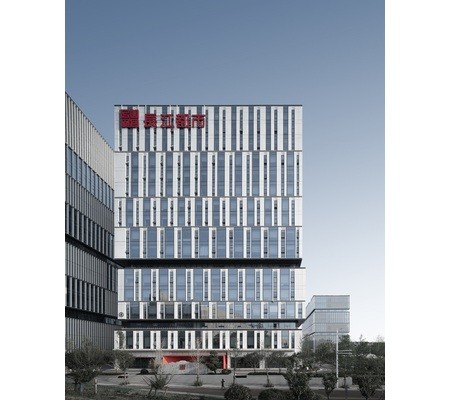
Guangdong Technion-Israel Institute of Technology (North Campus)
Last modified by the author on 23/03/2023 - 08:46
New Construction
- Building Type : School, college, university
- Construction Year : 2016
- Delivery year : 2018
- Address 1 - street : 大学路 515000 汕头市, 中国
- Climate zone : [BWh] Subtropical dry arid
- Net Floor Area : 102 237 m2
- Construction/refurbishment cost : 568 111 976 ¥
- Number of Pupil : 1 073 Pupil
- Cost/m2 : 5556.81 ¥/ m 2
Certifications :
-
Primary energy need
50.65 kWhpe/m2.年
(Calculation method : Experimental calculation method (China) )
Guangdong Israel Institute of Technology (North Campus) started the program design work in 2013, with the goal of high quality development of green building, and the whole life cycle concept has been carried out, and the project has been certified with the Green Building Evaluation Standard GB/T 50378-2014 3-star green building design and operation mark respectively. Now the post-evaluation is carried out using the Green Building Evaluation Standard GB/T 50378-2019 and the Green Campus Evaluation Standard GB/T 51356-2019, which can also basically reach the three-star standard. In order to provide replicable cases for similar projects, the monograph "Green Campus - A Chronicle of the Construction of Guangdong Israel Institute of Technology (North Campus)" was published.
I. Biophilia design
The campus is surrounded by mountains and water, and greenery is introduced through elevated space, platforms, connecting corridors and sky gardens, constituting a three-dimensional and active research and innovative campus atmosphere and spatial feeling; by preserving and improving the original topography, vegetation and water system of the site, a Lingnan garden landscape with Chaoshan characteristics is created; the mountain scenery of Sangpo in the northern neighboring area is reflected with the water scenery of the campus, and the mountains and water blend together, creating a green ecological campus with sustainable development.
II. Comprehensive planning of water system
The water system of the site is planned in an integrated manner, and the artificial wetland in the campus landscape is created by retaining and improving the existing water system before the development of the site; for the replenishment of the artificial wetland, the reservoir water of Shantou University next to the site is used for replenishment; at the same time, the artificial wetland is used as a rainwater storage pond, and the purified water is used for greening and irrigation of the site and road washing, and the greening and irrigation system also adopts micro-sprinkler system and sets The green watering system also adopts micro-sprinkler system and is equipped with humidity sensor, which is connected to the campus intelligent system for unified management.
III. Active and passive energy saving
The buildings are oriented to meet the summer wind direction, and the office building and the teaching building are set up with elevated floors to direct the summer wind to the internal courtyard, so as to avoid a hot and windless space. In winter, the winds turn northerly, and the teaching and research buildings block most of the winds from the northwest and northeast, so that the courtyard does not feel cold and windy.
In terms of daylighting, the buildings are connected on the short side so that they do not block each other in the north-south direction as much as possible, leaving sufficient daylight for working hours. Offices and classrooms with high requirements for sunlight are placed on the south side of the building as much as possible.
The building structure is mainly a reinforced concrete frame structure with a partial steel structure. Self-insulating bricks are used and a green roof is set up to effectively reduce heat transfer.
In terms of active energy saving, the project selects multi-connected air conditioning and primary split air conditioning system according to the building characteristics, which can be ventilated by opening windows at any time and can effectively reduce the air conditioning load. The installation of light guide tube lighting system in the underground space of the campus can help reduce the energy consumption of underground lighting.
IV. Smart Operation
The energy management system provides itemized statistics for air conditioning, lighting, power consumption and campus water consumption for the whole project. There are also intelligent control systems for elevators, air conditioners, irrigation systems and other equipment to help property managers be able to manage the campus efficiently.
V. Post-user Evaluation
The university hired a third-party professional team to analyze the focal issues in the form of on-site surveys and questionnaires, and put forward optimization suggestions conducive to improving the evaluation of campus satisfaction, complementing the existing campus construction from the perspective of meeting users' needs, and providing guidelines for future campus optimization and renovation as well as the construction practice of the new campus.
Data reliability
3rd part certified
BIM approach
The project adopted BIM technology in the design phase and construction phase respectively, and won the second prize of the second BIM application competition in Guangdong Province in 2018.
During the design stage, the BIM team intervened in the work and firstly formulated a service plan and determined the workflow according to the project characteristics. After the multi-disciplinary BIM model was built, the BIM team firstly carried out pipeline pre-arrangement for areas with narrow space and dense pipelines, simulated their implementability and put forward targeted optimisation plans, and assisted the design unit to complete several design modifications.
The building shape of this project is mostly irregular, and there are many professional systems and it is difficult for different professional construction to cooperate. In order to completely solve this technical problem, the construction phase was carried out through BIM technology to check the collision of various professions and comprehensive layout, correcting design conflicts and proposing more than 100 design optimisations, ensuring the coordination and unity of various professions during the construction process and achieving a seamless docking between design and construction.
Through BIM technology, it has effectively helped the project management to achieve fine management of project construction, and achieved digital, collaborative and integrated management of progress, drawings, contracts and cost modules.
Photo credit
Shenzhen Lvda Technology Co., Ltd.
Contractor
Construction Manager
Stakeholders
Contractor
汕头市政府投资项目代建管理中心
Shantou Agency Management Center of Municipal Government Investment Project is responsible for managing the construction of civil buildings and municipal infrastructure projects invested by the municipal government.
Thermal consultancy agency
深圳市绿大科技有限公司
Shenzhen Lvda Technology Co., Ltd. is a green building whole process technical service company, responsible for project planning, design, construction, testing and operation of green building consulting work.
Contracting method
General Contractor
Allocation of works contracts
Macro packages
Building users opinion
Thermal comfort and light environment: the building has a large number of openable area for external windows, allowing effective use of natural ventilation and natural light. Each functional room is equipped with independently adjustable air conditioning ends (multi-connector, split air conditioning), which can adjust the indoor thermal environment according to individual preferences.
Air quality: The indoor air quality of the building is good and odourless.
Sound environment: The main source of noise in the North Campus is traffic noise, and there is noise pollution from external air-conditioning units in the aisles on the ground floor. In the construction of the North Campus, the envelope of the building meets the sound insulation requirements as far as possible, the teaching area and the administrative area both adopt multi-connected air conditioning units, and the building equipment is uniformly set up and isolated from the use space, so there is no noise pollution.
Energy consumption
- 50,65 kWhpe/m2.年
Envelope performance
- 1,29 W.m-2.K-1
Real final energy consumption
34,80 kWhfe/m2.年
2 021
Systems
- Others
- Heat pump
- Solar Thermal
- Others
- Natural ventilation
- Double flow
- Solar Thermal
- 10,25 %
Smart Building
Biodiversity approach
Urban environment
Entrance/Exit and Public Transport:
The main entrance/exit of the project is located on the north side of Shantou University Road, which is close to the main traffic artery of the project. The distance from the site entrance to the bus stop is 260m on foot, reaching the Shantou University bus stop on the west side of the project and 240m on foot to the Longquanyan bus stop. The main routes passing through Shantou University Bus Station are No. 6, No. 17, No. 21, No. 27, No. 39 and No. 41; the main stops passing through Longquanyan Bus Station are No. 6, No. 17, No. 21, No. 27, No. 39, No. 41 and No. 107.
Public service facilities:
Activity venues are open to neighbouring residents on a staggered basis, supporting facilities are shared, resources are shared and open public space is available to the public, with specific measures as follows:
1. Before 8am and after 6pm, nearby residents and the public can use the outdoor venue for free for fitness and recreational activities.
2. Within 1000m of the site, there are 5 or more services such as canteens, entertainment, supermarkets and leisure, cultural and banking facilities to serve the students and teachers in the living areas of the project.
3. The canteen, entertainment, supermarket and sports and recreational space are free of charge for the students and teachers in the school area and the surrounding residents.
Activity space:
The campus is divided into living area and science and education area according to functional zoning. In the planning stage, through wind environment simulation analysis, terrace, courtyard and overhead space are used to divide the campus, so as to form smooth outdoor airflow while ensuring functional zoning. In summer, outdoor wind can be blown into the campus through the overhead corridor to avoid forming a windless area; in winter, the mountain on the north side is used to block the cold winter wind, and the wind speed is less than 5m/s through the measured data in winter.
Green area:
The actual green area rate of the campus is close to 40%. The large green areas are utilized to echo with the small green areas scattered in the campus, with the planting landscape in different courtyards, forming a staggered greening atmosphere. The landscape water body can be used as a tandem factor to connect the campus areas. Two through water systems are distributed in the middle and north of the campus, surrounding the administration building, which not only can cool down the campus in the hot summer, but also add some lively atmosphere to the campus. The courtyards of different sizes are enclosed between the buildings on the campus. The courtyards with permeable grounds become open spaces for students and teachers to discuss, communicate and relax, while the courtyards with shrubs or landscaping facilities constitute quieter semi-private spaces, maximizing different functional needs and enriching the space for campus activities. At the same time, the Sampo Mountain on the north side brings a natural landscape to the campus.
Ecological design:
The project is designed to focus on the interrelationship of landscape spatial pattern and spatial processes. The landscape spatial pattern is composed of elements such as patches, substrates, corridors and boundaries. As a space used by students and teachers for a long time, the ecological landscape design can integrate the surrounding natural landscape with the school space, which has a positive effect on the physical and mental health of the space users. The ecological landscape design of the campus focuses on "mountain", "water", "courtyard" and "corridor In the design of the campus ecological landscape, the four dimensions of "mountain", "water", "courtyard" and "corridor" are used to create a campus landscape with local Lingnan characteristics by combining the Sangpo Mountain around the project and the original water system and vegetation in the site.
"Mountain" - The layout of low south and high north is adopted to cater to the mountain to the maximum extent. The planning layout of the campus follows the topography and strives to create a garden-style campus space. In order to maximize the introduction of landscape into the campus, the building height gradually rises from south to north, while the building shape gradually tends to be free from the regular form - buildings near the south side of the road are arranged parallel to the road, with a more regular interface toward the city; buildings near the mountain in the north have a lively and diverse shape, with a free and permeable façade and mountain view The buildings near the mountain to the north have a lively and diverse shape, with a free and transparent façade that interacts with the mountain view, allowing students and teachers to have a rich landscape view and a rich and interesting spatial experience inside the building.
"Water" - connects to the water body in the form of a garden landscape and provides a public platform for rest and communication. The plan arranges diverse and lively shared spaces along the water side of the base. These active spaces freely dot the campus and form a dialogue with the mountain with a permeable interface, which includes functions such as exhibitions, coffee, club activities, and small lecture halls. It provides a comfortable and natural space for academic communication among students and faculty.
"Courtyard" - The buildings are linked together in the form of courtyards, allowing people to move freely through each space. The buildings of different functions on the campus form several similar but different "courtyards". In the scripture of "Zhou Yi", the building is classified as Yang and the courtyard is classified as Yin, and the combination of reality and fiction gives us the "front garden" and "backyard", which can greatly improve the infectious power of the building group. The concept of courtyard is integrated into the design of the green campus, and the clever use of indoor and outdoor gray space allows students and teachers to mingle with the natural elements of light, wind and rain as they wander through the courtyard, and as the axis linking these courtyards looks from east to west, people can feel the extension and continuation of the campus courtyard space.
"Corridor" - the corridor runs through the whole and provides a landscape platform for communication and rest. According to the climatic characteristics of the Chaoshan region with high temperature and rain in summer, the campus design draws on the design technique of the unique coastal bridge township with its modern architectural characteristics of the cavalry building, combined with its outer corridor type building The corridor is completely open and connected to the street corridor, forming a continuous and sheltered traffic space between the street and the buildings. At the same time, the setting of gray space enriches the sense of hierarchy and interest of the ground floor space, providing an efficient transportation corridor and a beautiful "sight corridor" between the "courtyards". At the same time, the second floor provides an open viewing platform, which runs through the courtyard and is hidden from time to time to experience the change of scale of different spaces. The deck is partially considered as a planted roof with wood flooring to harmonize with the natural color of the mountain.
Land plot area
68 565,80 m2
Green space
21 919,00
Product
MCM (Modified Clay) new ecological material

广东福美软瓷有限公司
MCM (Modified Clay) is a new ecological material with the advantages of being true to nature, flame retardant, breathable and non-discolouring. The possibilities of MCM (Modified Clay) eco-materials are not limited to this, it can replace cement, asphalt, polyurethane, rubber, wood and resin, the heat needed to produce the material is the waste gas from the power plant, the warm water cooled down can be used as domestic water, the whole line is almost zero pollution. It is a "breathable" eco-material, so to speak.
The product is made of inorganic materials such as waste soil, cement blocks, porcelain slag and stone powder, which are mixed and modified by classification, and shaped under photochemical isomorphism and curve temperature. It has good resistance to direct light irradiation, acid and alkali salt corrosion and mild characteristics. The compounded soil has a good plasticity and can be made into various sheets, blocks, rolls and profiles under photochemical isomorphism and controlled curve temperature.
The material can be 'customised' according to the customer's requirements and can be compounded into a variety of imitation stone, imitation terracotta tiles, imitation wood, imitation metal and other products, which can be used in a wide range of scenarios. The material is clay modified, from clay modification to low temperature baking, to final forming, no harmful gases and other pollutants, so when used in indoor scenarios, it has no impact on indoor air quality. The soft porcelain technology products (MCM materials) are mainly used in the decoration of the interior and exterior walls of various buildings and are particularly suitable for high-rise buildings as well as old wall renovation projects as they are soft, thin, light and very safe.
Construction and exploitation costs
- 568 111 976 ¥
Energy bill
- 2 471 500,00 ¥
Water management
- 29 044,00 m3
- 3 245,00 m3
Indoor Air quality
Comfort
Quality of life and services
The pedestrian passages within the project site are designed to be barrier-free and meet the relevant requirements of the Barrier-Free Design Code GB50763-2012. The pavements, public green areas, public service facilities and supporting public buildings of the project are all designed to be barrier-free, with the longitudinal slope of the pavements not greater than 2.5%, and the entrances and access roads of public green areas at all levels and facilities such as rest pavilions have a gentle and non-slip plane; the entrances and exits of public service facilities and supporting public buildings are sloped.
General infos
1. improving the thermal insulation properties of the envelope;
2. installation of external shading systems to reduce summer air conditioning energy consumption through the adoption of different external shading measures;
3. the use of energy-efficient air-conditioning, electrical appliances, lifts and other indoor energy-using equipment;
4. adopting passive design for part of the structure and using natural ventilation to reduce the energy consumption of the air-conditioning system
5. rationalisation of air conditioning system operating hours and lighting switching times to minimise carbon emissions and energy consumption during the operational phase of the building;
6. the use of a large number of highly recyclable green building materials such as steel and timber structures in some of the buildings to minimise the carbon emissions generated during the building demolition phase;
7. the selection of materials for the project is tailored to local conditions, minimising carbon emissions during the transportation phase of materials, etc.
Carbon sink
Local building materials: The proportion of local building materials (within 500km) used in the project is at least 80% by weight.
Initiatives promoting low-carbon mobility
The university encourages green transport such as public transport and bicycles. Motor vehicle parking is strictly controlled throughout the campus, and bicycle parking spaces are provided on the overhead level of the buildings to provide parking spaces for non-motorised vehicles that can be shaded from the sun and rain.
GHG emissions
- 235,75 KgCO2/m2/年
- 13,41 KgCO2 /m2
- 50,00 年
- 11 804,10 KgCO2 /m2
Reasons for participating in the competition(s)
1) Environmental benefits
The application of energy-efficient materials and green building technology in the North Campus of Guangdong Israel Institute of Technology effectively saves the economic cost of construction, improves the ecological environment of indoor space and enhances the comfort of space, making it a model work of green campus project. The annual electricity saving is about 1563420 kWh, which translates into an annual saving of about 809069 kg of standard coal, an annual emission reduction of about 1227264.7 kg of carbon dioxide, and an annual emission reduction of about 121739 kg of SO2.
2) Social benefits
At present, China's environmental pressure is increasing, and there is an urgent need for scientific and appropriate green building technology and experience. This project is an important demonstration for the application and demonstration of new green building technologies in the southern region (passive building, non-traditional water use, green campus, information-based property management, etc.), fully reflecting our corporate spirit and social responsibility of focusing on the industrialisation of green building.
3) Economic benefits
The project adopts a series of active and passive energy saving measures. After one year of operation, the total energy consumption of the building is 3465562.10 kWh, saving approximately RMB1,127,600 in electricity costs compared to the energy saving benchmark value, which greatly saves the operating costs of the campus. The campus energy consumption monitoring platform can be used in the later operation process to provide timely statistics and analysis of the campus energy consumption data, and to regularly optimise and upgrade the equipment to ensure good operation.
The campus adopts first-class water-saving appliances and intelligent watering system, and the campus landscape uses non-traditional water sources, so the annual incremental benefit of water consumption is about RMB 90,000, which achieves a more significant economic benefit. The water saving equipment is regularly serviced and the campus intelligent management platform is used to detect leaks in a timely manner.
Building candidate in the category