Look back on the webinar: "Renewable electricity and innovative heating networks to decarbonise European cities!"
D2Grids Project

Wednesday, November 02, 2022, was held the webinar co-organised by Celsius Initiative and D2Grids, whose objective was to explore the possible synergies between renewable electricity and innovative district heating and cooling grids.
While only 19.1% of the EU's building and industrial energy is supplied by renewable sources, the heating and cooling sector accounts for 50%!, 5GDHC grids mainly relying on heat recovery and renewable and local energy sources have a key role to play in energy transition!
The webinar was divided into four parts: first, Herman Eijdems, Mijnwater's Innovation Director, reminded about 5GDHC concept, which D2Grids aims to promote in North-West Europe. Mathilde Henry then explained how solar energy, and in particular PV, can be used in these heating and cooling rids. A roundtable implying representatives of the pilot sites experimenting this kind of project had the opportunity to tell us more about their plans. Finally, Nina Jacobsson Stålheim presented the concrete case of Gothenburg city in Sweden and its use of solar electricity and their heating and cooling grids.
In this article, you will discover the key information of the webinar, as well as its video replay and the PowerPoint used by speakers.
5GDHC is the most advanced generation of heating grids to this day. Its particularity is that it uses an energy recovery and redistribution system that is not only decentralised but also redistributed through pipes incorporated in a low-temperature loop, recovering, and redistributing the energy within the users of this self-regulating loop.

Learn more about the 5GDHC principles
D2Grids project has also developed key performance indicators to assess heating grids according to these principles. This allows to understand the evolution perspectives for all heating grids.
Learn more about these indicators
The example of the first 5GDHC grid in Herleen in the Netherlands highlightsthe effectiveness of this concept:
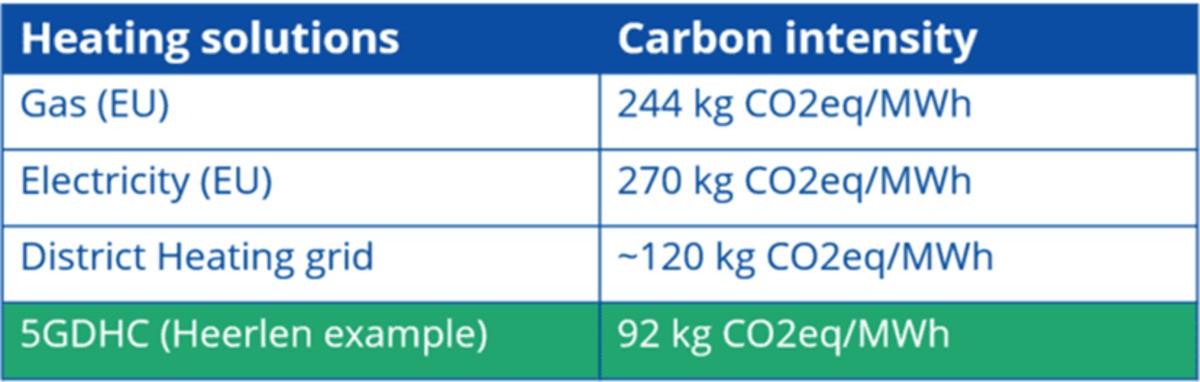
Thus, the future perspectives are now to develop and increase the number of innovative heat grids, getting as close as possible to a 5G system by lowering the temperature of the network, reducing the maximum power, and saving energy.
Producing renewable and local solar electricity such as photovoltaics avoids electricity peaks and obviously the use of fossil fuels. It is also beneficial to protect oneself from increases in electricity costs due to an unstable context!
It is therefore necessary to develop financial, contractual, governance and business models. D2Grids pilot sites are working to develop best-practice models for this purpose.
These were the topics discussed during the roundtable with representatives from three D2Grids pilot sites.
For example, the social landlord SEQENS recently joined D2Grids with a unique project of collective self-consumption photovoltaic production by connecting to the heating and cooling network of Paris-Saclay.The electricity produced and not consumed by its buildings will be sold to the heating and cooling grid.
Finally, Nina Jacobsson Stålheim explained that the city of Gothenburg in Sweden has already integrated a solar energy plan by installing solar panels on all suitable roofs in the city by 2030. The additional electricity will be sold back, allowing the city to be completely energy independent and get a good return on investment.
About D2Grids and Celsius Initiative
As a reminder, the European D2GRIDS project aims to develop 5th generation heating and cooling grids in North-West Europe.
Celsius Initiative is a demand-driven collaboration for efficient and integrated heating and cooling solutions, supporting cities in their energy transition to carbon neutral systems.
paul.capgras[a]construction21.fr




