ENSM : Maritime School of Le Havre
Last modified by the author on 19/05/2017 - 11:01
New Construction
- Building Type : School, college, university
- Construction Year : 2015
- Delivery year : 2016
- Address 1 - street : 76600 LE HAVRE, France
- Climate zone : [Cfb] Marine Mild Winter, warm summer, no dry season.
- Net Floor Area : 11 242 m2
- Construction/refurbishment cost : 18 960 000 €
- Number of Pupil : 650 Pupil
- Cost/m2 : 1686.53 €/m2
Certifications :
-
Primary energy need
-0.6 kWhep/m2.an
(Calculation method : RT 2012 )
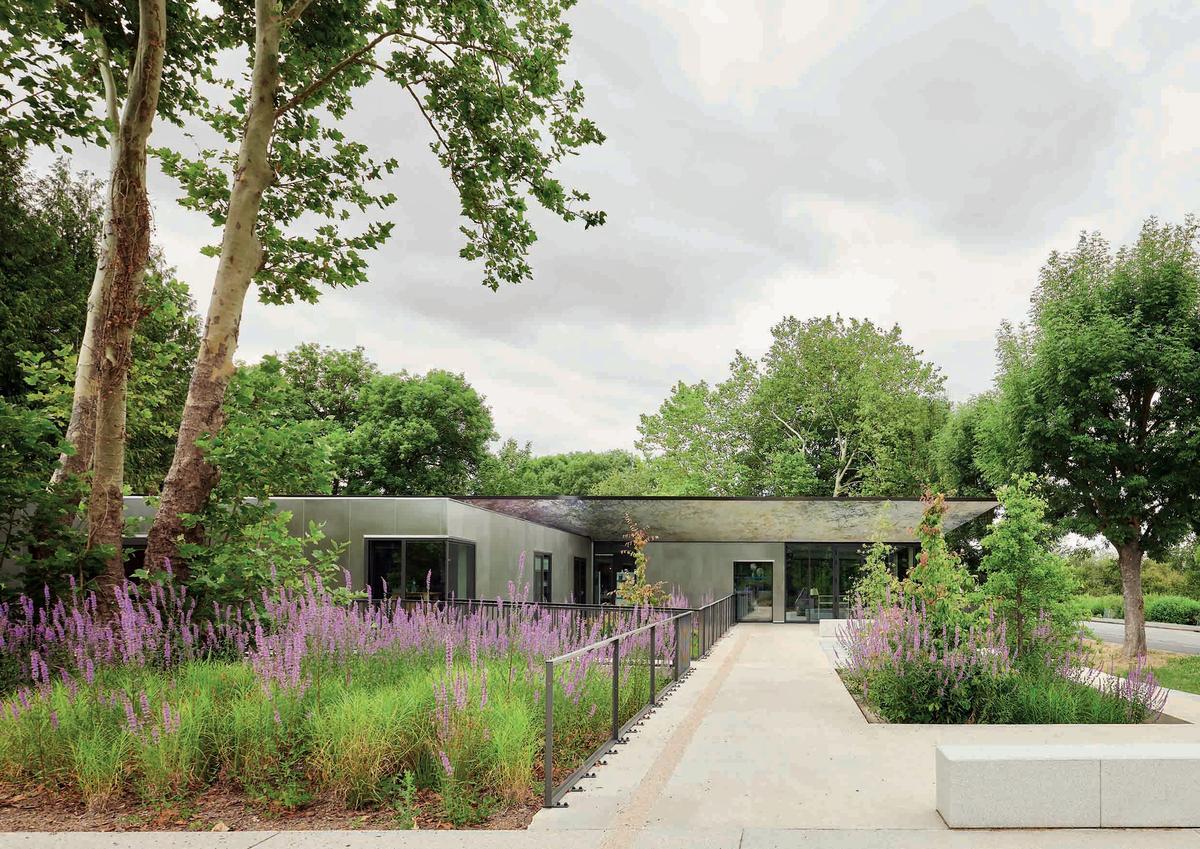
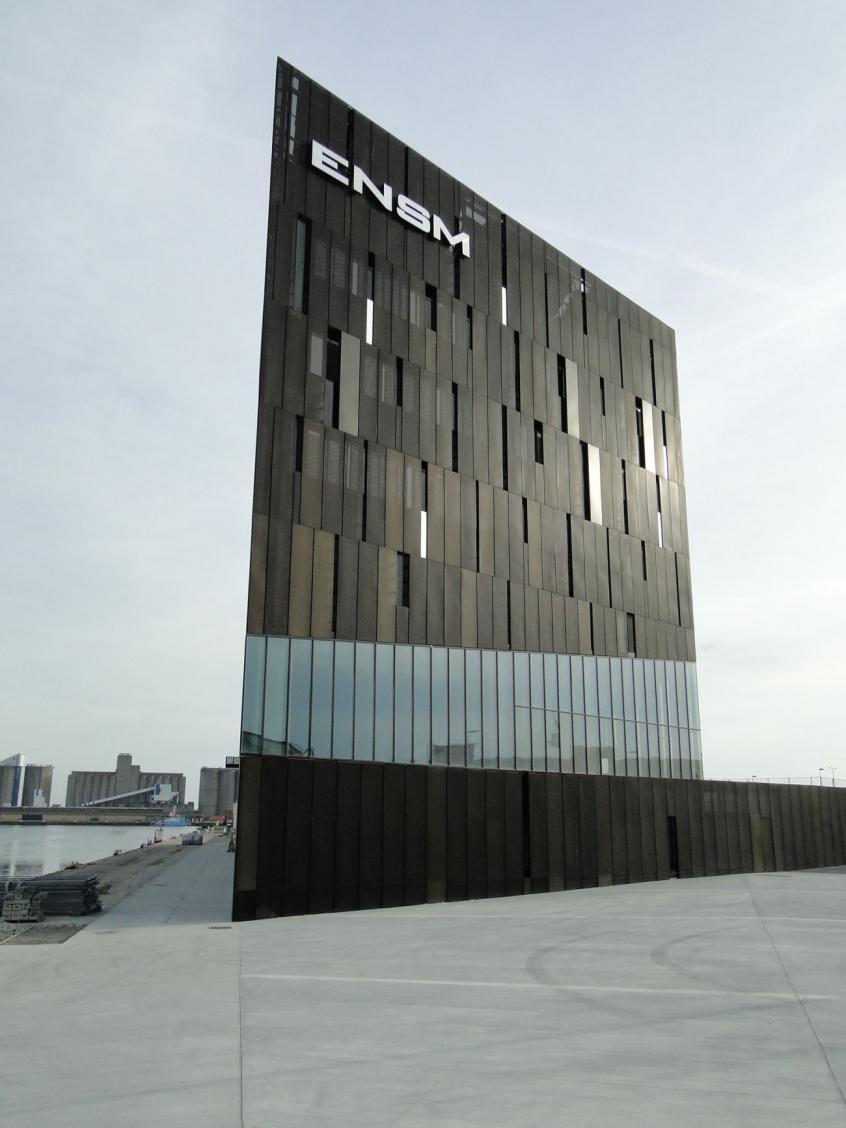
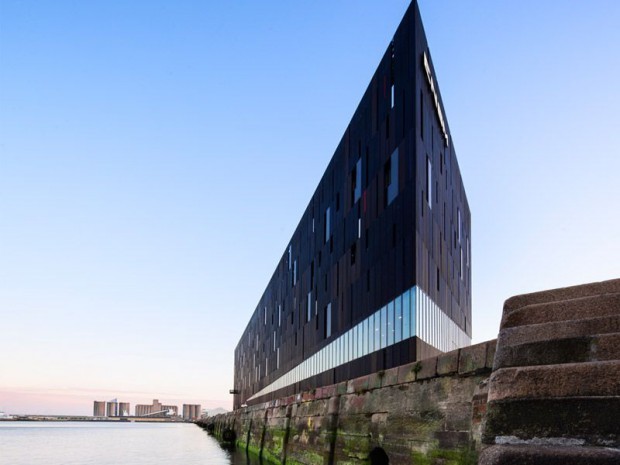
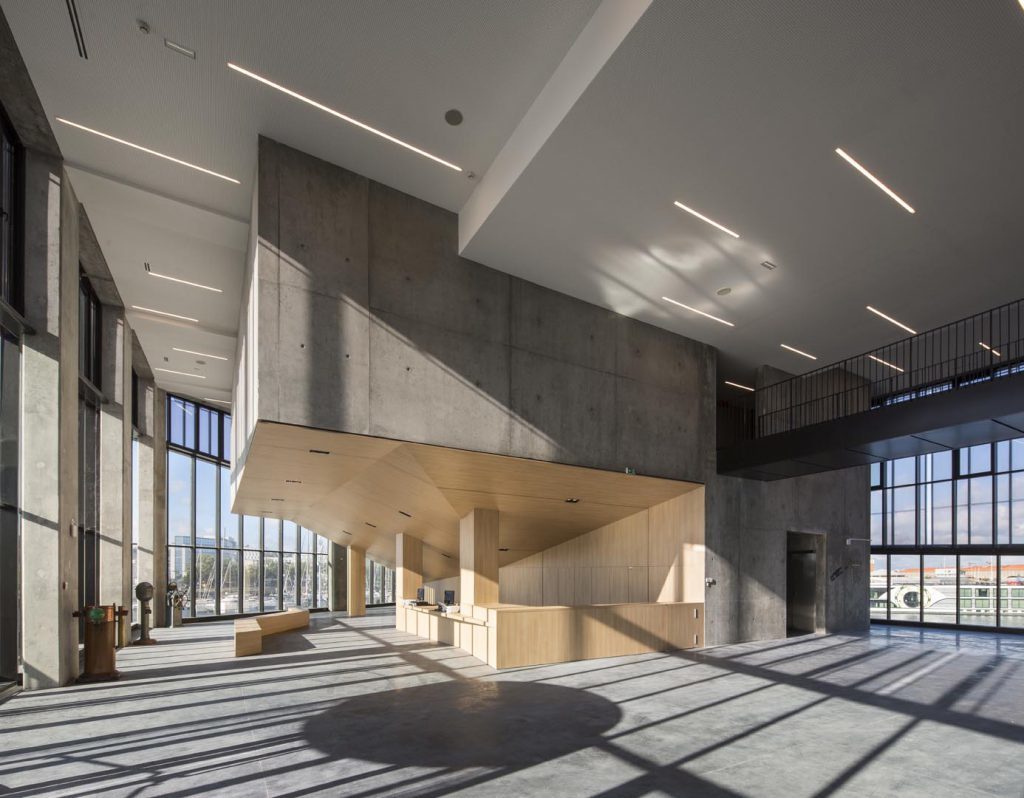
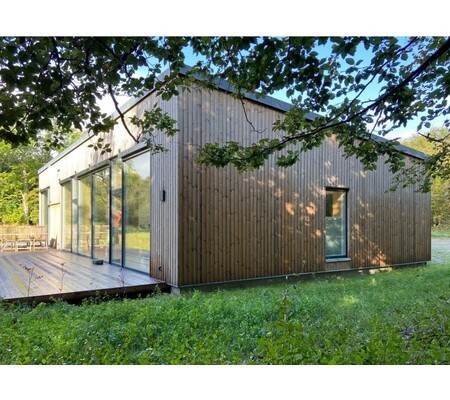
A 100m long building evoking the silhouette of a ship's bow and configured as a training ship, will accommodate 650 pupils / year. It has 7 levels on almost 10 000 m². This project was carried out by Sogea Nord Ouest, a subsidiary of VINCI Construction France.
Sustainable development approach of the project owner
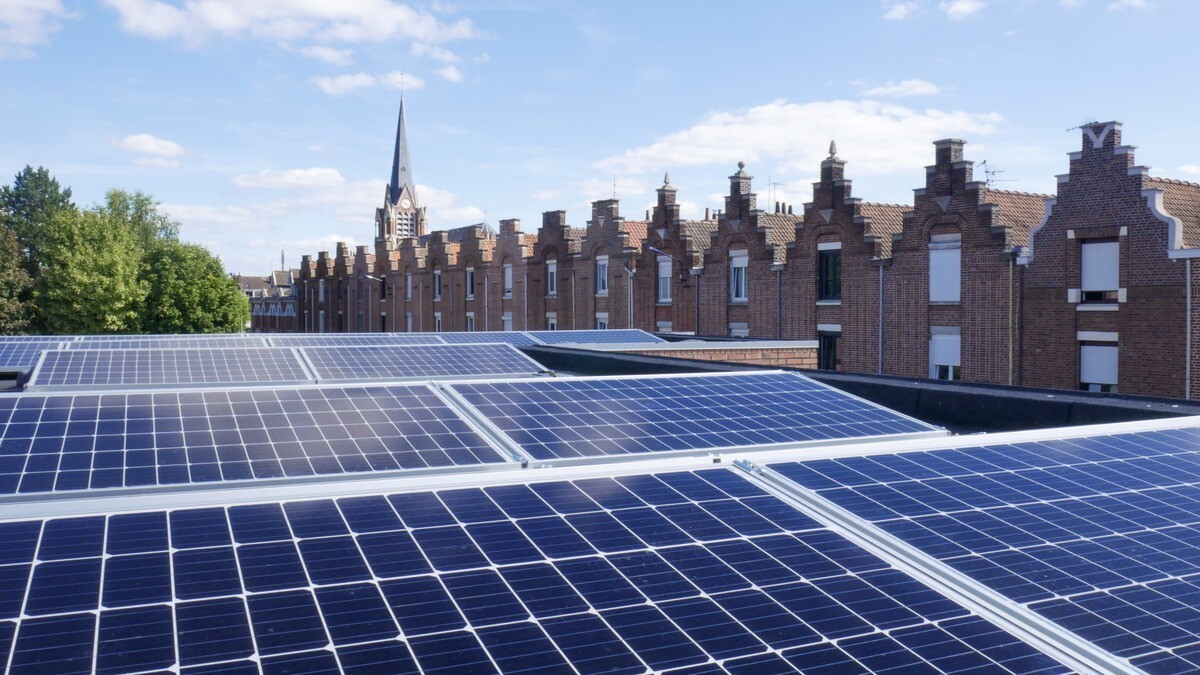
Sustainable Development is a theme that the CODAH is already looking to integrate, with exemplary approaches to project management. With the construction of the ENSM, many environmental parameters have been optimized, such as the environmental footprint (Carbon Footprint), energy autonomy (SMART GRID ready building). In particular, the autonomy of the building in resources has been particularly thorough until achieving a high environmental performance, through the exploitation of solar and maritime renewable energies. The use of seawater for cooling (via the geocooling process) and the heating of the building (via a heat pump with high energy efficiency on seawater) is a special feature of this project. This results in a building whose energy balance is positive, mostly thanks to the implementation of a photovoltaic roof.Architectural description
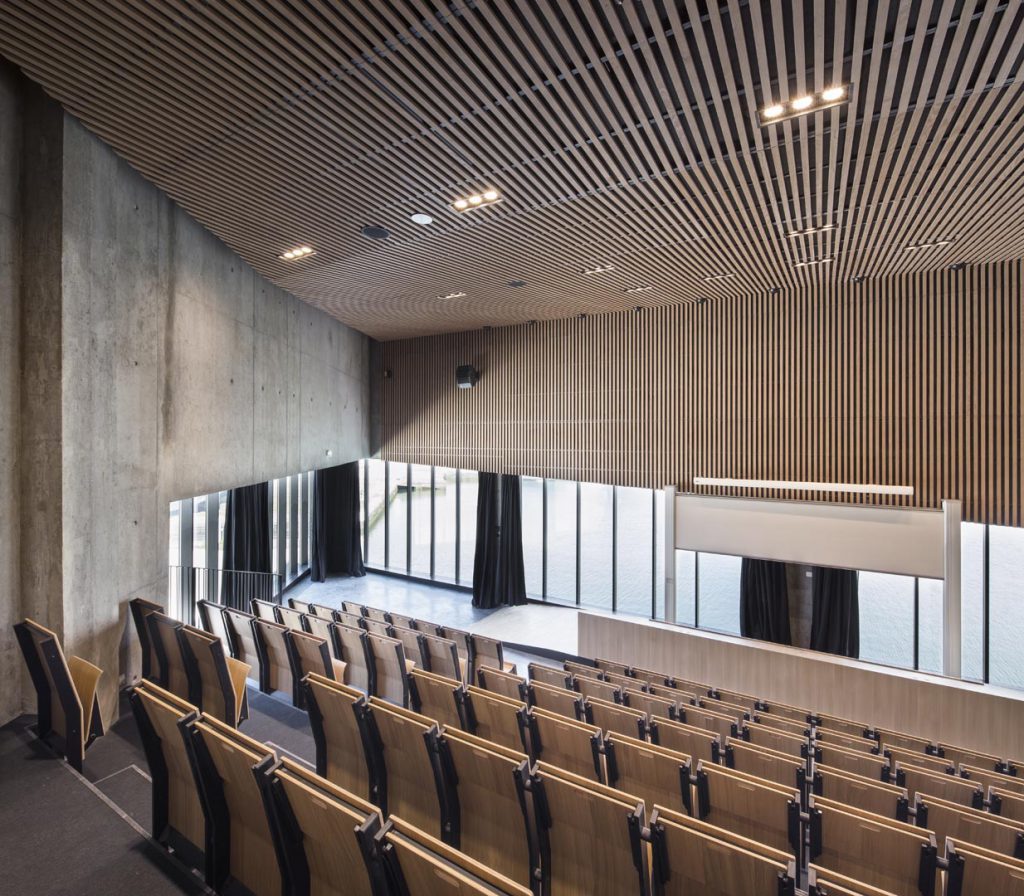
The pupils are immersed in open sea conditions closest to the real world, including machine simulation rooms, a marine engine and a dozen 'walkway' simulators distributed over three levels. The architectural bias of AIA is to consider the whole school in the spirit of a "school ship". The whole structure is thus configured: from its forecourt to the gangway of embarkation until the ascent to the upper deck through the engine room, the technical rooms located in hold, the sixteen rooms and Four amphitheatres overlooking the basin. Beyond the specific spaces of the program, the different interior spaces are treated in the spirit of those of a ship where the presence of the technique is everywhere visible and omnipresent.See more details about this project
http://www.vinci-construction.fr/oxygenStakeholders
Designer
AIA Associés
http://www.a-i-a.fr/Other consultancy agency
ECHOS
http://www.beechos.com/Design office for eco-design of buildings
Company
SOGEA Nord Ouest
Contractor
Communauté de l'Agglomération Havraise (CODAH)
Construction Manager
AIA Ingénierie
http://www.a-i-a.fr/ingenierie/Energy consumption
- -0,60 kWhep/m2.an
- 71,50 kWhep/m2.an
Systems
- Geothermal heat pump
- Water radiator
- Other hot water system
- No cooling system
- Double flow heat exchanger
- Solar photovoltaic
- Heat pump (geothermal)
Urban environment
Product
PAC 6 tubes ERACS 1302 W-Q

CLIMAVENETA
http://fr.climaveneta.com/Web/HVAC, électricité / heating, hot water
The Heat Pump features:
- a base and a supporting structure made of hot-dip galvanized steel sheet
- a control cabinet with a main disconnect switch (according to EN60204-1 /
IEC204-1)
- a CLIMAVENETA W3000 microprocessor controller with dry contacts: On / Off and
Synthesis of defects + screen interface
- 2 semi-hermetic screw compressors with power modulation of 50 to 100% or 3
(50, 75 and 100%). These compressors are equipped with de-oiler, suction valve,
Discharge and a heating resistor crankcase.
- of 3 R134 exchangers / multitubular water
· An evaporator, which makes it possible to produce the refrigerating energy
· A condenser (called RECUPERATOR in the supplier data sheet), which allows
To produce calorific energy
· An exchanger (called the CONSENT in the supplier data sheet), which allows
To evacuate the surplus calorific or refrigerating energy (via a valve 3
Modulating channels).
These 3 heat exchangers are equipped with a differential pressure switch, thermally insulated and equipped with
electrical resistance.
- a MODBUS communication card for communication with the GTC
- flow controller on each exchanger
Reasons for participating in the competition(s)
Avec la construction de l'ENSM, de nombreux paramètres environnementaux ont été optimisés, tels que l'empreinte environnementale (Bilan Carbone), l'autonomie énergétique (bâtiment SMART GRID ready).
En particulier, l'autonomie du bâtiment en ressources a été particulièrement approfondie jusqu'à atteindre une haute performance environnementale, via l'exploitation des énergies renouvelables solaire et maritime. L'utilisation de l'eau de mer pour le refroidissement (via le procédé de géocooling) et le chauffage du bâtiment (via une pompe à chaleur à haute efficacité énergétique sur eau de mer) est une vraie particularité de ce projet. Ceci aboutit un bâtiment dont le bilan énergétique est positif, en majeure partie grâce à la mise en œuvre d'une toiture photovoltaïque.
Building candidate in the category

Energy & Temperate Climates