Refurbishment project of an Alqueria to get almost zero HVAC energy demand
Last modified by the author on 21/06/2017 - 18:38
Renovation
- Building Type : Isolated or semi-detached house
- Construction Year : 1930
- Delivery year : 2017
- Address 1 - street : - 46120 VALENCIA, España
- Climate zone : [BSk] Mid-latitude Dry Semiarid (Steppe)
- Net Floor Area : 120 m2
- Construction/refurbishment cost : 80 000 €
- Number of Dwelling : 1 Dwelling
- Cost/m2 : 666.67 €/m2
-
Primary energy need
14.38 kWhpe/m2.year
(Calculation method : Other )
The aim of this project is the refurbishment of a traditional Valencian orchard house, whose constructive typology is called Alquería, in order to achieve a negligible HVAC energy demand
The objective of this project was defined considering the current worldwide energy and environmental situation and the risen cultural interest for the traditional edifications.
With that purpose, an energy model was developed using energy software TRNsys 17 following these consecutive steps:
· First the necessary data sets such as climatic data and construction building characteristics were collected and studied.
· Then, an original housing energy model was performed in order to get a validation of the model (RMSE 1.63°C, MAPE 5.88%).
· After that, an energy optimization strategy was proposed. The following step was implementation of energy efficiency measures.
· Finally, the corresponding results were carefully analyzed.
The overall conclusions obtained from the analysis were:
a) A good matching of the energy model is fundamental in order to reproduce the specific thermal behavior of the studied building
b) Enhancing the building envelope is the most effective proposal to achieve the reduction in the HVAC requirements of the building.
Finally with the application of passive measures (measures applied to the building which do not require additional energy) was gotten zero energy demand of active air conditioning (Heating Demand: 0.7kWh/year m2, Cooling Demand: 2.2 kWh/ year m2).
A Blower Door test was carried out for the purpose of verifies if the tightness level is the appropriate according to the Passivhaus standard. The result was 1.49 renovations per hour, satisfying the tightness demand for building rehabilitation according the Passivhaus standard.
Presently, the project is in the phase of the construction process, remaining to be done some finished and the fitting of shadowing devices. Any active HVAC system and heating recovery haven't been implemented.Pretending supply the HVAC requirements with natural ventilation in summer and with passive solar heating.
Coming, temperature and humidity sensors will be placed into of the house in order to prove if the house really has a nearly zero energy HVAC demand.
Data reliability
Self-declared
Stakeholders
Designer
Ana Martínez
Developing energy model by means of energy software TRNsys 17. Energy analysis through simulation in order to chose the most effectiveness energy efficiency measures.
Owner approach of sustainability
Refurbishment of interest cultural house such as the Alquería, trying to keep its characteristics and by means of implementing passive energy measures, achieve a nearly zero HVAC energy demand.
Architectural description
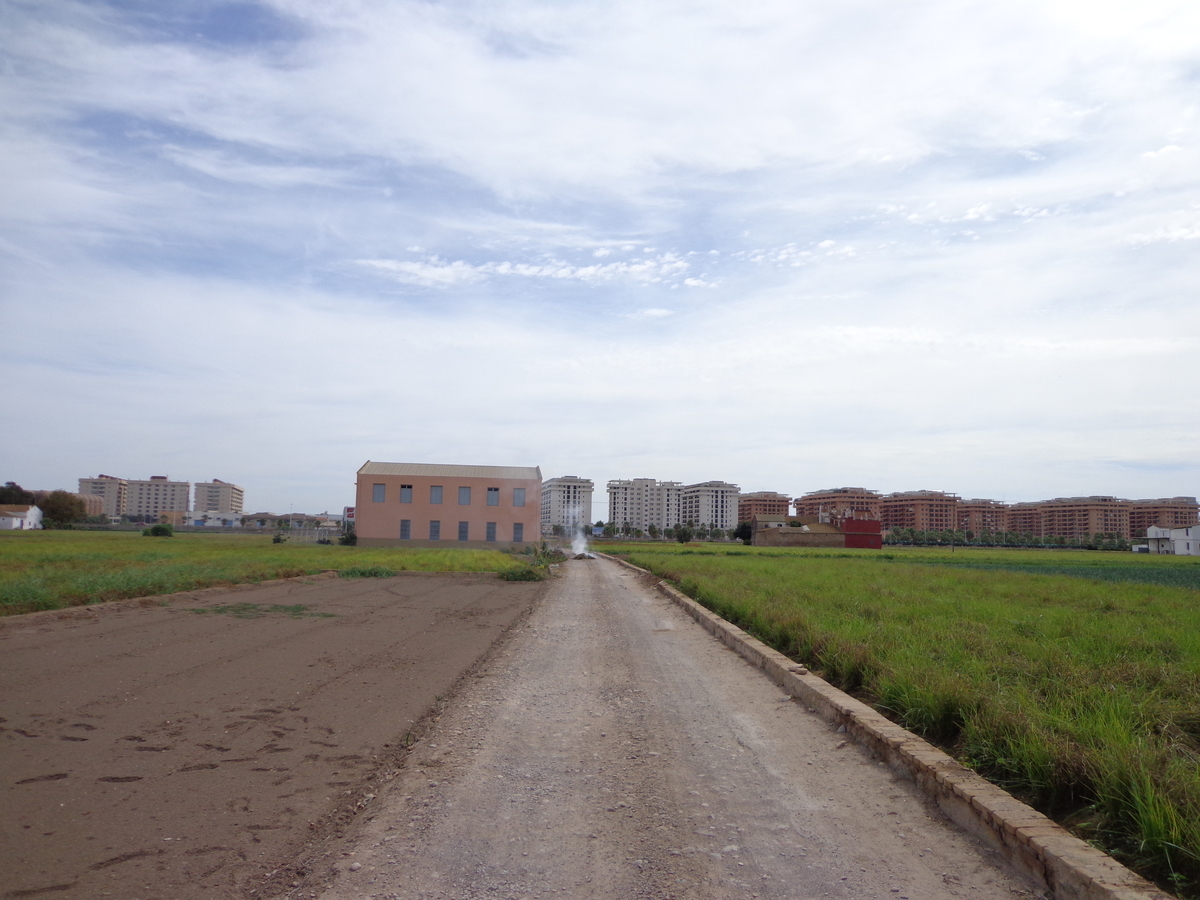
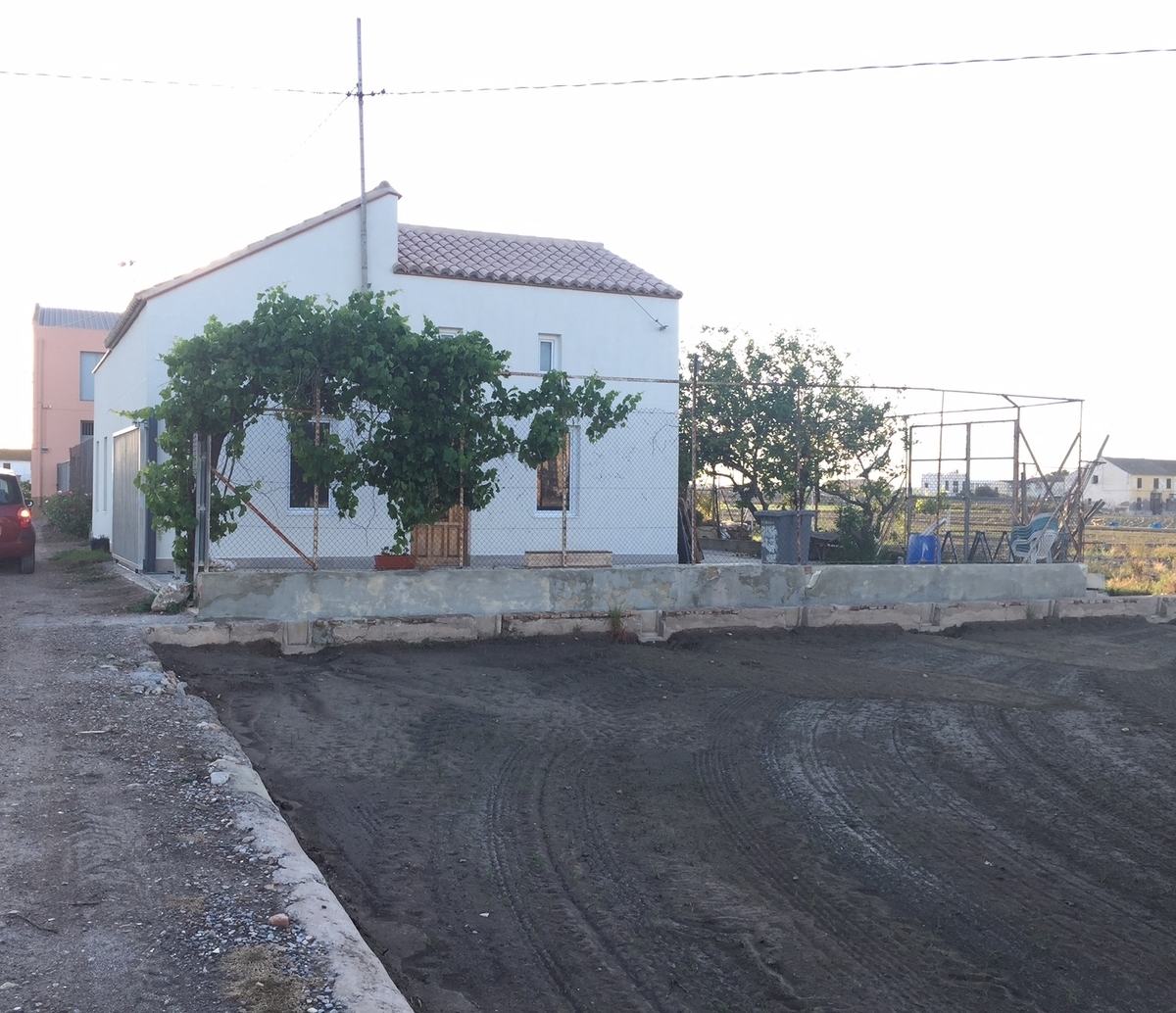
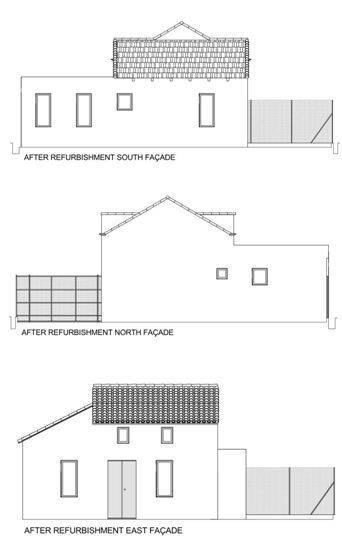
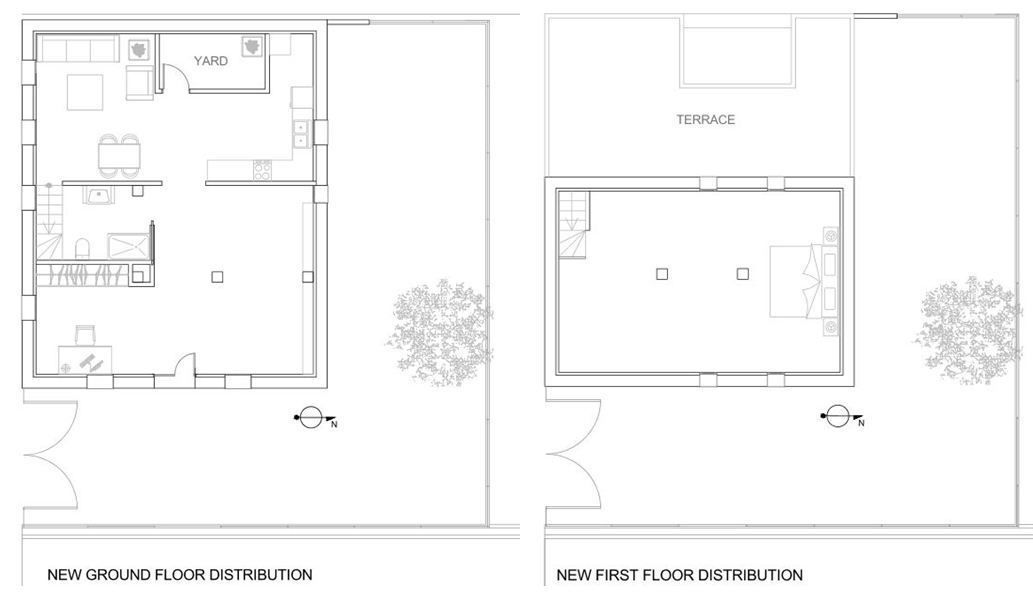
The house is a single isolated dwelling and consists of two floors, built in the first half of the XX century in the stage prior to the II Spanish Republic (1930). The house is located in a Valencian orchard, 820 meters from the Mediterranean coast, in the municipality of Alboraia (Valencia). The architectural typology is the modern alquería, a typical orchard farmhouse from the east and southeast coast of Spain and of Hispano-Muslim origin. Its main façade is orientated towards the east to take advantage of the breeze from the sea for ventilation and cooling of the farmhouse, especially during the summertime. These types of buildings were houses of tillage in which the ground floor was used as a house, and the “cambra” or zone under the roof was for the storage of the harvest or for the breeding of silk worms. The geometry of the floors was typically rectangular, or as in our specific case, it could attach two rectangles forming a 90˚angle. The ground floor of the house is 60 m2 in area and 2.8 m. high. Briefly, the constructive characteristics of the building are: solid brick masonry walls, without any thermal insulation. The floor and deck structure is made of wooden joists and beams. The pillars are solid brick. The south-facing shed roof is supported on the end gable of the roof east-west. The roofs are finishing with curved tiles. Previously to the house’s refurbishment, an energy simulation study was carried out in order to achieve a negligible HVAC energy demand house. The analyzed measures for reduce the HVAC demand, were: Passive energy efficiency measures: The thermal insulation of the whole building enclosure. Optimizing the windows area depending on the orientation. Selection of the best characteristics for the windows. Shading devices. Free cooling obtained from cross ventilation. Active energy efficiency measures: Heating recovery. Mechanical ventilation system. Through the simulation was gotten the best option of each measure, being the HVAC requirements results of the developed simulation model with all of the proposed measures implemented close to 0. Finally was decided not implementing heating recovery and mechanical ventilation systems in the building, only the passive measures will be implemented. On the other hand in the refurbishment of the house has been tried to respect as much as possible the original appearance of the dwelling and the materials. The structural consolidation of the building was needed. Due to its bad state, the deck was completely rebuilt, retaining its original typology, on its constructive elements. The intermediate floor was reinforced and was anchored to the walls. The walls in bad state were repaired following the original configuration. Briefly, the changes regarding to the original house, have been the following: Thermal insulation has been placed in all of the façades and the deck. In the walls has been disposed on the external face by means of SATE system. In the south façade the original windows and doors has been replaced for four windows in order to get a properly passive heating by means of direct solar radiation. For the purpose of avoiding overheating in windows facing to east, west and south orientation are going to be installed awnings. The type of windows has been substituted for tilt PVC windows with LowE double glass. The situation of the house enable good natural ventilation, therefore cooling requirements can be supplied by it.
Energy consumption
- 14,38 kWhpe/m2.year
- 54,52 kWhpe/m2.year
- 1,00 kWhpe/m2.year
Envelope performance
- 0,17 W.m-2.K-1
- 1,90
- 1,49
Systems
- No heating system
- Individual electric boiler
- No cooling system
- Natural ventilation
- Solar absorption chiller
Indoor Air quality
Comfort
Product
External Thermal Insulation Composite System
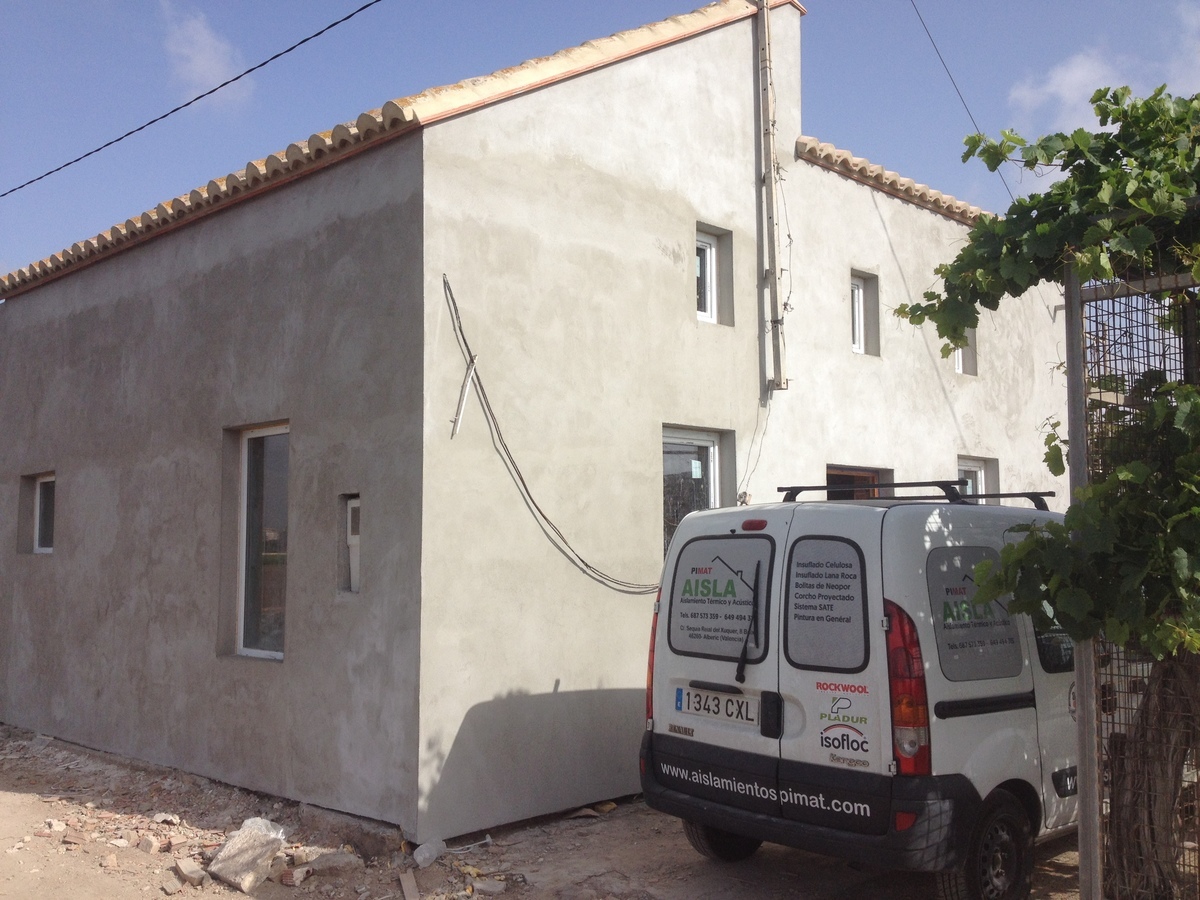

Aislamientos PIMAT
C/ Sequia Real del Xuquer 8, 46260 Alberic, Valencia
http://www.aislamientospimat.com/
The SATE System: External Thermal Insulation Composite System (ETICS), is an EPS system of thermal and acoustic insulation of facades by the exterior. While other insulation is incorporated to the façade by means of a work, the SATE System is a prefabricated insulation panel that adheres to the façades by means of a mixed fixation (by means of mechanical and adhesive fixing), which gives the façade of an enclosure Thermal insulation that improves energy efficiency and minimizes heat leakage and moisture entry.
As a result of its expanded polystyrene composition the SATE system is an insulation panel that provides thermal insulation on the exterior of the home. It also has a reinforced lining and acrylic mortar.
As a result, the SATE System (Exterior Thermal Insulation System) has these advantages:
-Thermal insulation that reduces the loss of heat in winter up to 70%.
-Thermal insulation that reduces internal heat in summer up to 30%.
-Acoustic isolation.
-Resistance to solar impact.
-Protects the facade of the weather (long durability).
-It guarantees the perspiration of the facade.
-Reduces the risk of condensation.
-Installation on the exterior of the facade (does not consume internal m²).
-Low maintenance cost (hardly needed).
-Raincoat.
-Incombustible (A1)
-100% natural
-Easy and quick to install
-Allows variety of finishes, even dark colors.
Therefore, PIMAT Insulation considers that this SATE System is a system of thermal insulation suitable for both new constructions and to rehabilitate deteriorated exterior façades as it provides a greater thermal and acoustic insulation capacity. In addition, it improves the resistance to external agents and hardly needs maintenance.
This product was very appropriate because it was been easy to install, and it presents a very high resistance to heat transfer.
Urban environment
The building is situated in a growing area closet to irrigation ditches, also is near to the coast and to the Universitat Politècnica of Valencia.
Building Environmental Quality
- comfort (visual, olfactive, thermal)
- energy efficiency